Medical Cannabis
The Story of Medical Cannabis
Medical cannabis has an extensive and diverse history that spans across civilizations. From its use in ancient cultures for both therapeutic and recreational purposes to the modern era of scientific exploration, the story of medical cannabis reflects the enduring quest to harness nature’s healing potential. It represents a journey marked by continuous discovery, where tradition meets innovation.

-5000 BC
Cannabis appears in several ancient medical treatises
Until the end of the 19th century
Traditional use of cannabis in medicine
1953
Withdrawal of cannabis from the French pharmacopoeia
1964
Identification of the constituent molecules of cannabis by Raphaël Mechoulam and verification of their effectiveness in treating various illnesses
1990
Discovery of the endocannabinoid system, which suggests that “the active principles of cannabis could be used to treat chronic pain and neurological disorders” (NASEM, 2017).
2020
The United Nations Commission on Narcotic Drugs recognised the therapeutic effects of cannabis.
Key Components
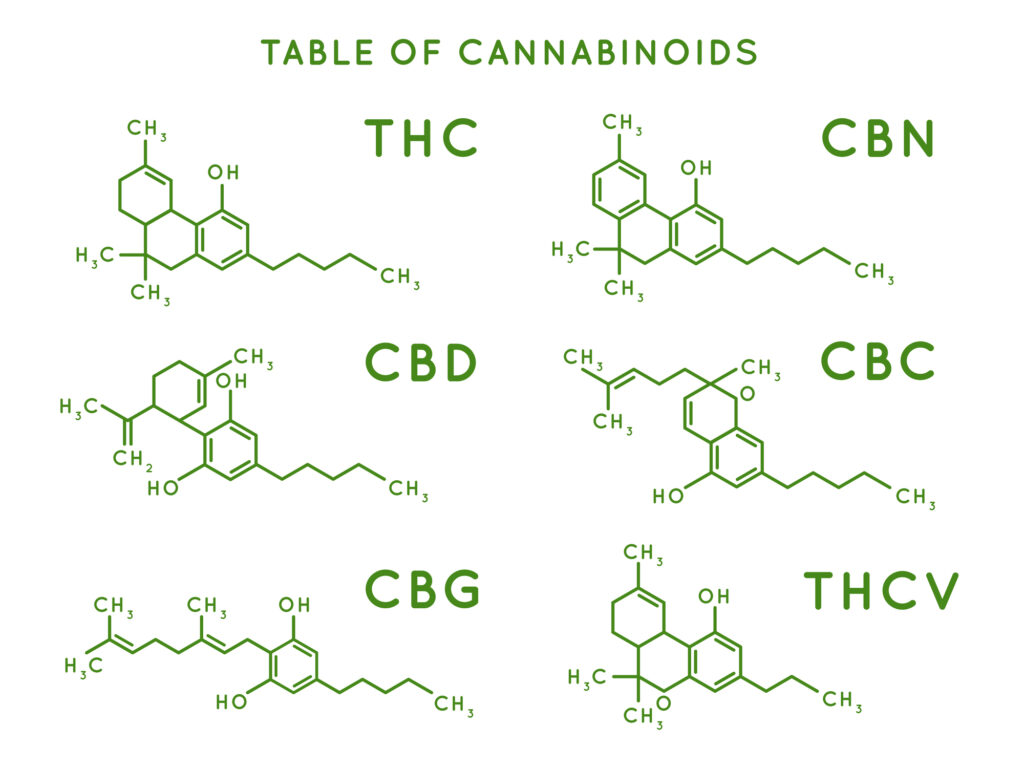
Cannabis is a complex plant, comprised of 545 distinct chemical compounds, with over 100 diverse cannabinoids being among the most noteworthy.
Extensive clinical research has demonstrated that numerous cannabinoids engage with the body’s cannabinoid receptors, exerting influence over a wide spectrum of physiological processes. Among the cannabinoids, Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) have been the primary subjects of extensive study due to their distinct pharmacological characteristics and immense therapeutic promise.
Understanding the key components of medical cannabis is pivotal:
- Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC): This psychoactive compound is responsible for the euphoric “high” often associated with cannabis. Beyond recreation, THC has demonstrated potential for pain relief, muscle spasm control, and stimulating appetite.
- Cannabidiol (CBD): CBD is non-intoxicating and offers a broad spectrum of potential therapeutic benefits. It’s been studied for its anti-anxiety, anti-inflammatory, and anti-seizure properties. The balance between THC and CBD is a fundamental aspect of tailoring treatment for specific conditions
Beyond THC and CBD, other compounds within the plant may play a role in its extensive range of beneficial effects. This includes minor cannabinoids like cannabinol (CBN), cannabigerol (CBG), and cannabichromene (CBC).
- Cannabigerol (CBG): belongs to the resorcinol class of compounds. It has been observed to stimulate appetite and offers anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and antioxidant advantages.
- Tetrahydrocannabinol acid (THCA): serves as the precursor to THC, and it’s regarded as non-psychoactive. Studies have indicated that THCA possesses anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. Furthermore, it has demonstrated efficacy in reducing nausea and vomiting.
- Cannabinol (CBN): arises as a metabolite of THC. CBN exhibits a preference for binding to cannabinoid CB2 receptors, primarily found on immune cells. There is speculation that CBN may possess immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Cannabichromene (CBC): is a cannabinoid compound devoid of psychoactive effects, and research has indicated its potential in exhibiting anti-inflammatory, pain-relieving, and activities akin to antidepressants.
Medical Uses
The scope of medical cannabis’s potential applications is vast:
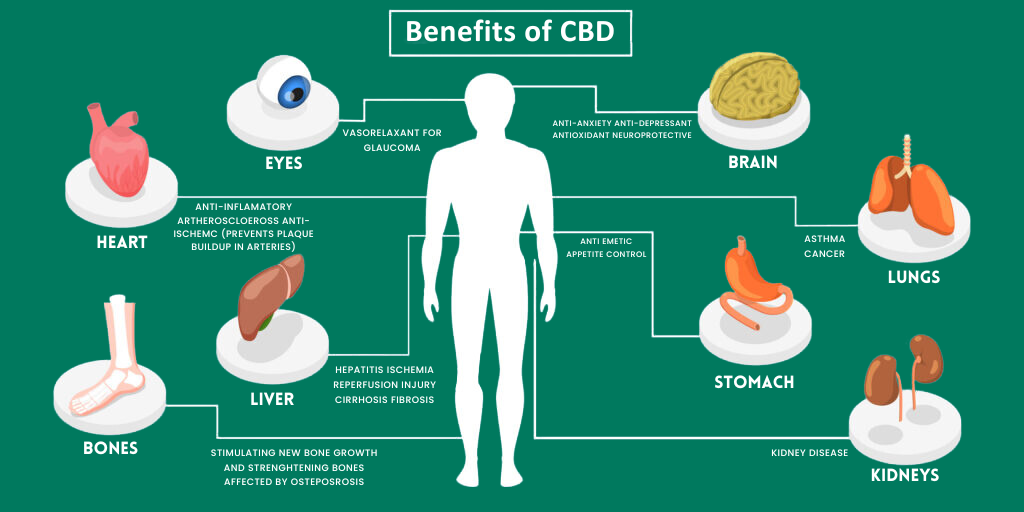
- Chronic Pain Management: For individuals enduring long-term pain, such as arthritis, neuropathy, or cancer-related pain, medical cannabis provides an alternative to traditional pain medications.
- Epilepsy and Seizure Disorders: Emerging as a promising treatment for individuals who don’t respond to conventional anti-seizure medications.
- Anxiety and Depression: Offering potential relief from symptoms and improving overall mental health and well-being.
- Multiple Sclerosis: Easing symptoms like muscle spasms, pain, and spasticity often associated with MS.
- Cancer-Related Symptoms: Providing relief from chemotherapy-induced nausea and improving appetite.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Offering anti-inflammatory properties and alleviating pain and gastrointestinal discomfort.
- Glaucoma: Lowering intraocular pressure to prevent vision loss.
- PTSD (Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder): Managing symptoms and improving the quality of life for individuals with PTSD.
Methods of Administration
A range of administration methods caters to diverse patient needs:
- Oral: Choose from capsules, tinctures, or edibles for easy ingestion.
- Inhalation: Smoking or vaporization ensures rapid relief by delivering cannabinoids directly into the bloodstream.
- Topical: Creams, balms, or oils are ideal for localized treatment and targeting specific areas of pain or discomfort.
- Sublingual: Tinctures placed under the tongue provide efficient absorption through the mucous membranes for quick relief.
Potential Side Effects
It’s paramount to work closely with a healthcare professional to manage potential
side effects and achieve an optimal balance for your specific needs.
While medical cannabis offers numerous benefits, potential side effects must be considered:
DRY MOUTH
Known as “cottonmouth,” it’s a common side effect.
Occurs in some individuals, especially with higher THC doses.

Change in
perception
Some users may experience altered perceptions or mood swings.
A temporary elevation in heart rate is possible.
Difficulty focusing or memory recall may be affected.
Some individuals experience increased or decreased appetite.
Dosing Considerations
Precise dosing is critical for achieving the desired therapeutic effects while minimizing potential side effects. Determining the right dosage is a complex process influenced by several factors, including the specific medical condition, individual response, and the type of product used. Starting with a low dose and gradually increasing it under medical supervision is the recommended approach.
Current Medical Cannabis Landscape
In recent decades, there has been a gradual and widespread acceptance of the medicinal potential of cannabis. A notable milestone in this journey was the United Nations (UN) Commission on Narcotic Drugs’ reclassification of cannabis in 2020 to recognize its therapeutic applications. As a result, the legalization of cannabis for medical use is on the rise not only in Europe but also across the globe. Nonetheless, it’s important to note that the regulations governing medical cannabis products differ significantly from one country to another.






